Research on Reliability Improvement of Power Devices
IKEDA Toru
KOGANEMARU Masaaki
Background and objectives of activities
To achieve a decarbonized society, fossil fuel vehicles are being replaced by hybrid, electric and fuel cell vehicles. In addition, the amount of electricity generated from natural energy sources such as solar cells and wind power is also increasing. The key device indispensable to these devices is the power module. The development and improved reliability of power modules are essential to the realization of a decarbonized society and cleaner urban air by shifting to zero-emission vehicles. Japan, along with Germany, holds a large share of the power module market, and it is important for Japan to capture the growing demand.
Summary of Activities
Power module failures can lead to major accidents and infrastructure shutdowns, so ensuring the reliability of power modules is an important issue. For example, wire breakage due to thermal cycling fatigue of aluminum wire bonds in power modules is one of the major problems in ensuring the reliability of power modules. Therefore, we are working to elucidate the mechanism and develop techniques to predict the lifetime of this problem. Interface delamination due to thermal fatigue between the encapsulating resin and the metal substrate in power modules is also a major problem. We are also developing technology to predict the lifetime of interface delamination.
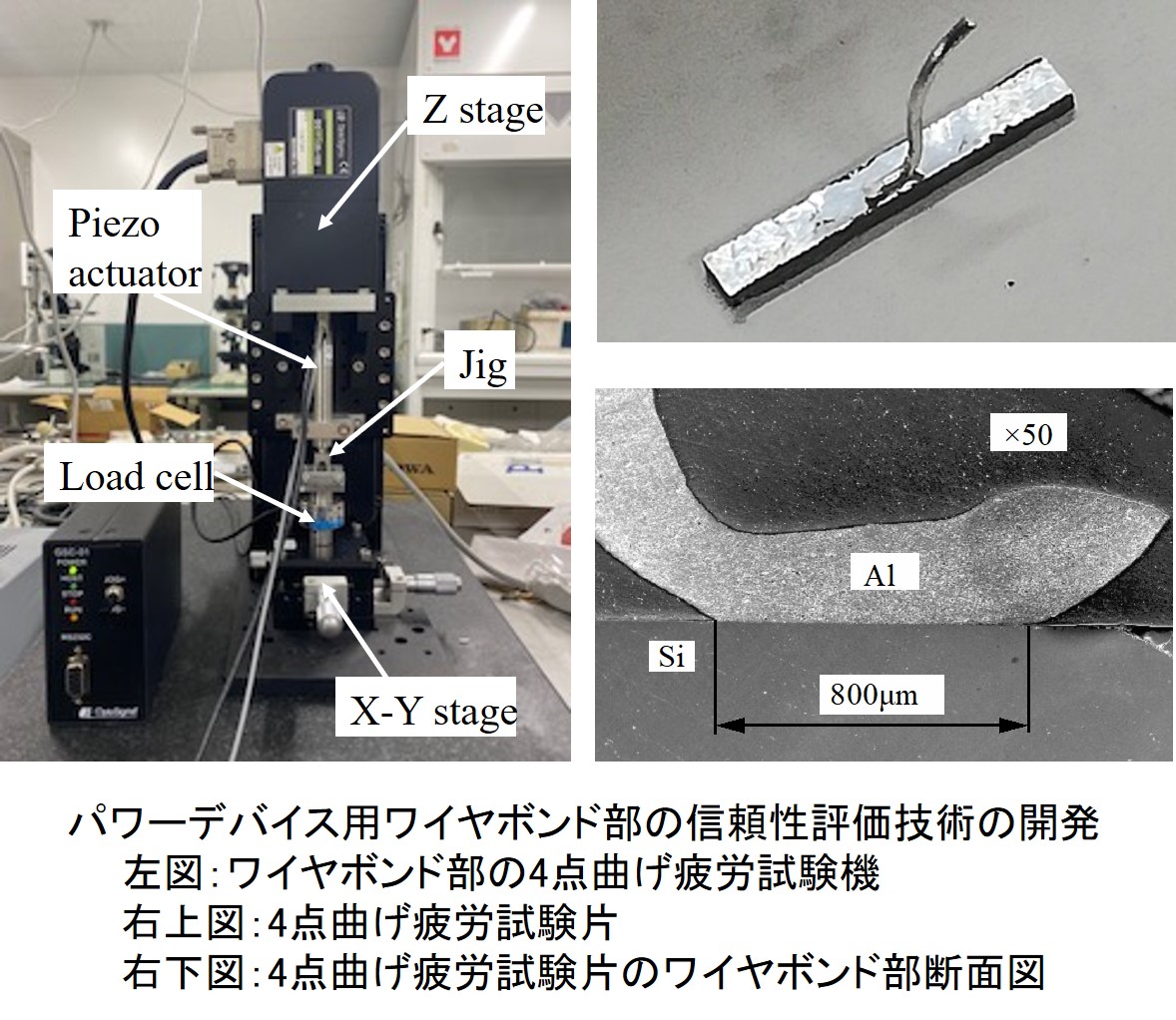
Expected Benefits
Power modules using wide-gap semiconductors such as SiC are beneficial for achieving the objectives mentioned in the Background and Objectives of the Activity because of their high efficiency and miniaturization, but ensuring reliability is more difficult than for conventional Si semiconductors. Therefore, improving the reliability of power modules is an essential technology for the widespread use of wide-gap semiconductors.
















